This series of topics will be a summary about System Design Interviews where we can tackle some topics and we can give abstract idea about it
This book is highly recommended
Today's topic will be about Scale from zero to millions of users
Designing a system that supports millions of users is challenging, it's a journey that requires continuous refinement and endless improvement.
in the following article we will build a system that supports a single user and gradually we will scale it up to serve millions of users.
Single server setup
Building a complex system always starts with something simple, lets start by running every thing in one single server
Figure 1-1 shows the illustration of running a single server setup where everything is running on one server(web app, database, cache, etc)
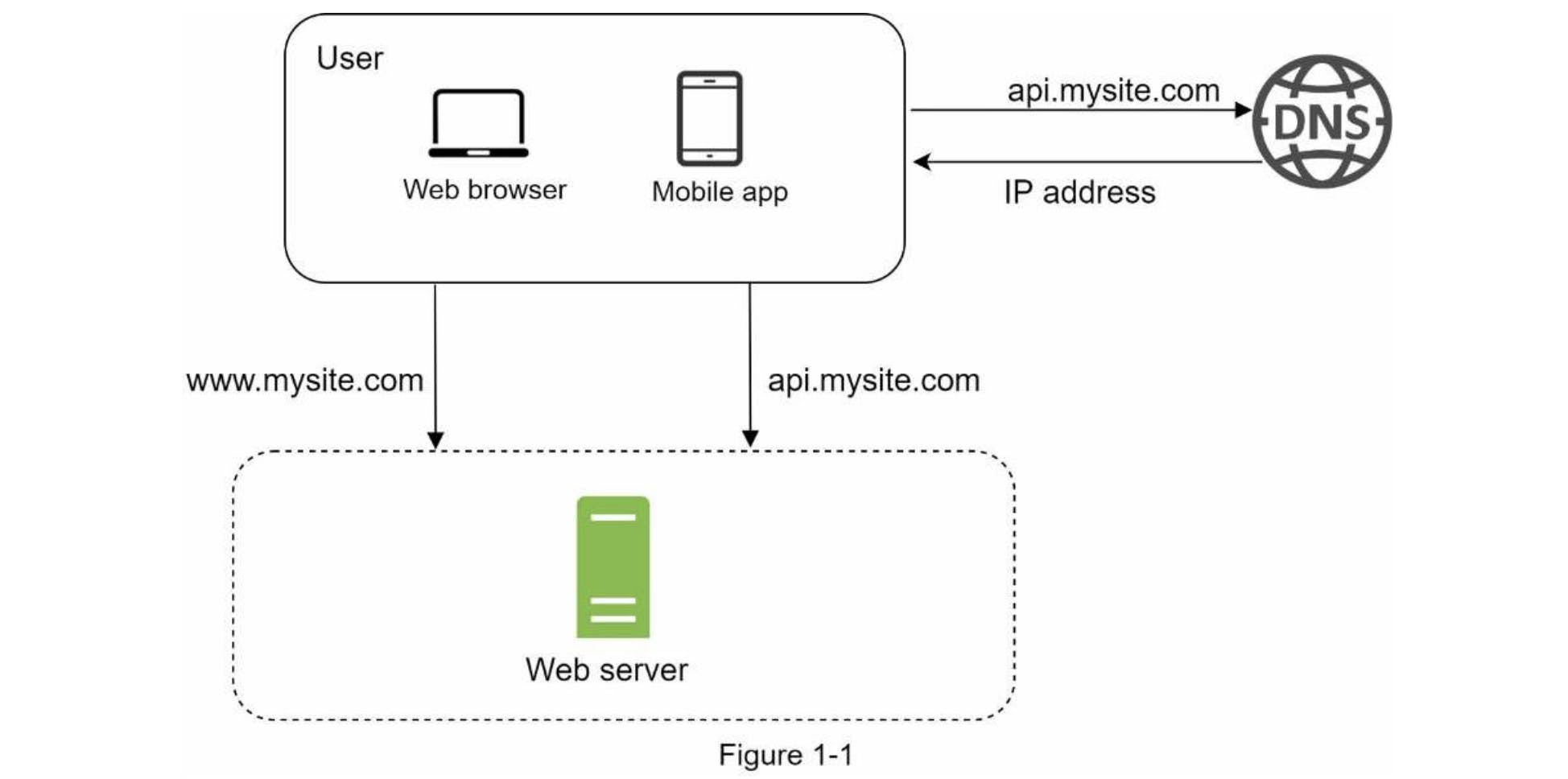
To understand this setup, it's helful to investigate the request flow and traffic source, lets take a look at the request flow first in Figure 1-2
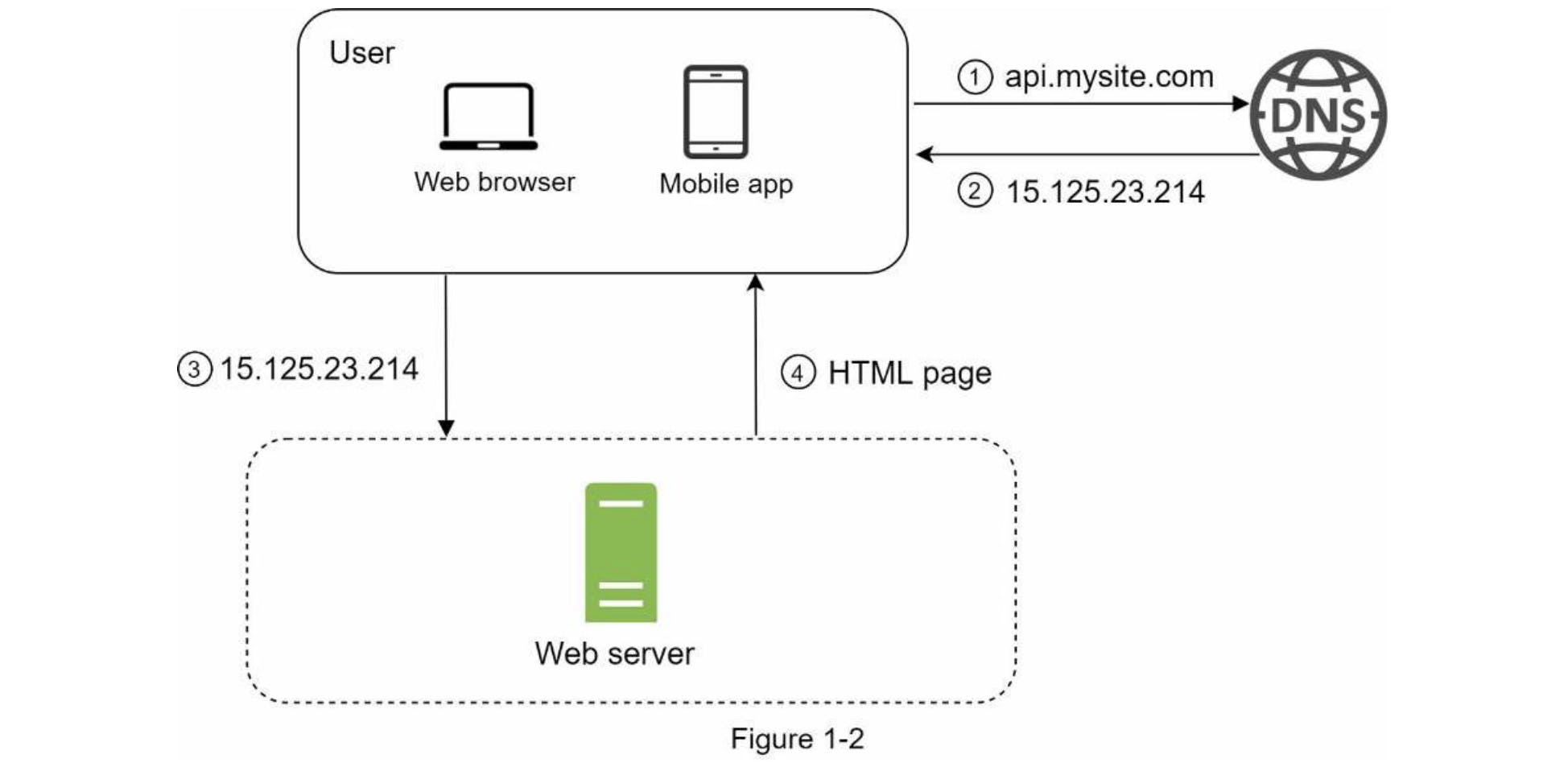
Users access websites through Domain names, such as "api.mysite.com.com". Usually The Domain Name System(DNS) is a paid service where it translates domain name to certain IP address.
Internet Protocol (IP) address is returned to the browser or mobile app.
once IP address is obtained, HTTP requests are sent directly to your webserver.
Webserver returns HTML pages or JSON response for rendering.
Next we can examine traffic source. the traffic to your webserver comes from two sources: Web application and Mobile application
Web Application most of the time it's a combination between server-side languages(ruby, java, python) for handling business logic, storage, etc and client-side languages (HTML and javascript) for presentation.
Mobile Application: HTTP protocol is the communication protocol between mobile app and web-server. mainly JSON(JavaScript object notation) is commonly used for API response
Database
As the users grow, one server is not good enough so we need a separate server where we can hold database
this separation technique where web tier(application + mobile) and data tier(DB) allows us to scale independently.
which database you chose?
Mostly Relational Databases or Non-relational Database. For most developers, relational databases are the best option right now, but it always dependes on the situation.
Non-relational Databases are used in one of the following cases:
- Your application requires to be low-latency.
- Your Data is not structured.
- Tends to save massive amount of data.
- Tends to serialize/de-serialize data (XML, JSON, YAML).
Horizontal Scaling vs Vertical Scaling
Vertical Scaling is the scale up operation by adding more (CPU, RAM, etc) to the server.
Horizontal Scaling is the scale out operation by adding more servers to the pool of your resources.
Load Balancer
It evenly distributes network traffic between web servers that are defined inside a load-balancer set
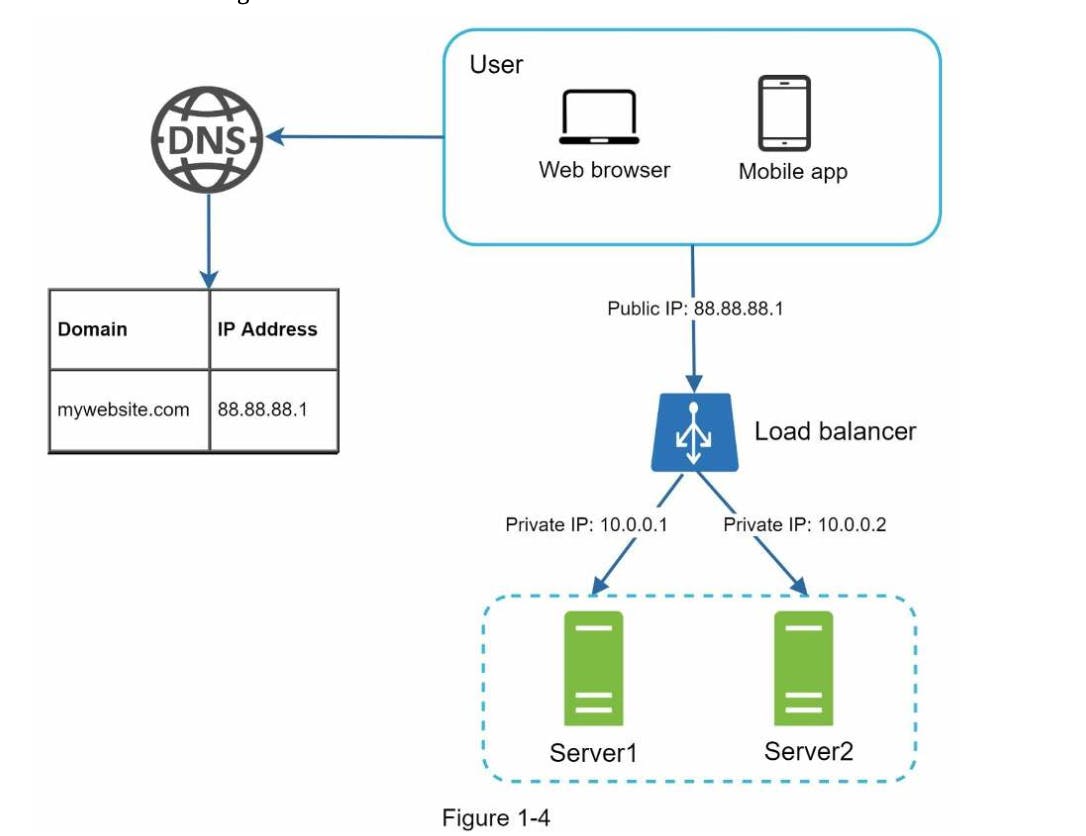
In figure 1-4 you can see a simple load balancer configuration. Users right now connect to public IP of the load balancer instead of web server directly, now web servers are not reachable by clients anymore.
So mainly Private IPs are used for servers for internal communication only For better security.
So by adding second server and a load balancer, we successfully solved fail-over problem and improved availability of web tier.
Now The web tier looks good, what about data tier, right now we have only 1 Database server where it doesn't support fail-over and redundancy. We can check now Database replication.
Database Replication
Database replication can be used in many Database management systems usually with master/slave relationship between the original(master) and the copies(slave). most of the applications requires higher ratio of reads to writes.
Master DB supports write operations.
Slave DBs supports read operations.
Advantages
Better Performance because this model allow read queries to be processed in parallel. Better Availability because if one server is destroyed, data already is replicated on another sever. Better Reliability
So after designing the following architecture where we integrated load-balancer, Database replication and Horizontal scaling. It is time to improve load/response time, this will be done by adding a cache layer and shifting static content (JS, CSS, Images and videos) to the CDN(Content delivery network)
Cache
is a temporary storage area that stores a result of expensive response or frequently accessed data in the memory, so any future requests can be served more quickly
So every web page is loaded, one or more database calls are executed to fetch data, the application performance is affected by calling database repeatedly, so adding a caching tier could solve the problem.
Cache tier
is a temporary storage layer, much faster than database. It is added for better system performance by trying to minimize Database hits.
Considerations for using cache
Decide when to use cache
Expiration policy
Consistency: this involves keeping data stored and the cache in sync
Mitigation failures: A single cache server represents a potential single point of failure (SPOF), so multiple cache servers accross multiple data centres could actually solve the problem
Eviction Policy: Once the cache is full, any other requests to add item to the cache could cause existing data to be removed, to solve the following problem we need one of the following techniques
LRU: least recently used.
FIFO: First in first out.
In the next article we will complete the rest of the chapter.